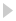
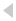
Pure AK features

East German MPi-KM and KMS-72 Rear Sight Bases (Revised v1.3)
Sunday, August 26, 2012

Among the subtle details of interest to the AK enthusiast is variation in production design of a single model. Hardly a year went by at any Warsaw Pact arsenal where some AK component was not modified in order to save weight or production expense. East German produced stamped-receiver AKM-type rifles, known as MPi-KM, were no different. These modifications were minor enough to not require a change in model designation, but can be used to determine the vintage of an AK even when a stamped date is not present or visible. One component that changed design at least six times over the production life of the MPi-KM was the rear sight base.
Production of MPi-KM rifles began in East Germany in 1964 and continued until a short while after the end of the DDR in 1990. MPi-KM rifles are different than most other AKM-pattern variants because of the use of a rear leaf sight graduated for ranges up to 800m. AKM-pattern variants typically use a 1000m rear sight, while AK-47 types usually 800m.
The East Germans chose to retain the 800m sight in their stamped-receiver rifles in order to keep the operation and zeroing procedures standardized with AK-47-pattern milled rifles already in their inventory. In addition, the East German military had invested in training devices for rifles equipped with 800m sights.
Rear Sight Base variants are listed below. Years listed are based on known examples, and do not necessarily indicate production of that variant started or stopped with the calendar year.
The pattern of the rear sight base does not always corollate with the year of original manufacture, as the East Germans were known to conduct extensive rebuilds of damaged rifles, sometimes replacing the rear sight bases of older rifles with current-pattern ones. This was particularly true when rebuilding Soviet-supplied AKM rifles with 1000m rear sights.
There may be exceptions to the years given, or even variations not listed here. I would be interested to hear about them.
Copyright © 2012 Stephen Miles
East German rear sight bases pictured with period NVA soldier-oriented publications. Variants of the Soviet AKM produced in East Germany were designated “MPi-KM” in NVA service and were produced from 1964 through 1990. During this period at least seven incremental changes were made to the design of the rear sight base. (Images Source: Author)


LEFT: In this image both milled (MPi-K, foreground) and stamped (MPi-KM, background) rifles are in use. Notice the mirrored aperture mounted on the rear sight leaf that allows the trainer to view the sight picture of the shooter. (Image Source: DDR State-owned “Visier” Magazine)

RIGHT: Contents of an East German ZGK-65 squad marksmanship training kit. Some devices in this kit are optimized for use with 800m sights. (Image Source: Author)



AKM Pattern: These rear sight bases for 1000m sight leafs were in use on AKM rifles first supplied to the NVA by the Soviets in 1961. Image is of a Soviet-supplied 1961 AKM later blued by the East Germans. (Image Source: Author)
First Pattern (1964-1966): While the first East German MPi-KM rifles were assembled in 1964 with predominantly Russian AKM parts, a new rear sight base was designed to accommodate the same 800m rear sight used in East German AK-47-pattern rifles. This design was essentially an AKM-pattern rear sight base with lengthened pads for the slider of the shorter 800m sight to rest on in the battlesight position. Image is of a 1965 MPi-KM cutaway. (Image Source: Dan Erik)
Second Pattern “Early Pinhole” (1966-1974): One of several production modifications applied during 1966, the design of the holes at the sight leaf hinge was changed to the small “pinhole”, while the profile of the rear sight base remained the same as the AKM-pattern. Image is from a 1966 MPi-KM. (Image Source: Author)
Fourth Pattern “Early Figure-eight” (1976-86): This design changed the design of the rear sight leaf hinge hole to a “Figure-eight” shape, and featured a simplified rear sight base profile. Image is of a 1976 MPi-KMS-72 captured and parkerized by the Isrealis. (Image Source: Author)

Fifth Pattern “Late Figure-eight” (1987-1988): The distinguishing feature of this variation is the simplified gas tube lever, otherwise identical to Third Pattern. Image is of an 1987 MPi-KMS-72 (Image Source: Author)
Sixth Pattern “Rough Cut” (1989-1990): In order to reduce costs, production of the MPi-KM rear sight base was co-located with the production of the MPi-AK-74 series rear sight base. Tooling at this new facility frequently made rough cuts on the sides of the rear sight bases of both rifles. This variation returned to a profile similar to that of the AKM, and also used the simplified gas tube lever. Images to right are of a 1989 STG AKM-K export pattern rifle.
(Image Source: Dan Erik)

FROM LEFT TO RIGHT: Russian 1000m AKM Sight, DDR “Red Letter” 800m Sight used until about 1966, DDR “White Letter” 800m, Sight used on all NVA MPi-KM/KMS-72 after 1968, DDR 1000m “K” Sight used on DDR MPi-AK-74N as well as some exports and prototypes.(Image Source: Author)


Export Pattern: Beginning in the early 1980s, some export rifles were equipped with 1000m rear sight leafs and compatible rear sight bases. These rear sight bases were originally very similar to the Soviet AKM pattern, and later adopted the simplified gas tube lever and “Rough Cut” of the Sixth Pattern. Image at right is of an export or prototype 1983-85 production MPi-KMS-72. (Image Source: Internet Scan)
Third Pattern “Late Pinhole” (1974-75): For this very short lived variation the rear sight base was modified with a simpler profile. This image is of a 1975 MPi-KM with a bakelite lower handguard replacing the original wood. (Image Source: Peter 13)




“Late Pattern” MPi-AK-74N: This rear sight base is almost identical to the “Rough Cut” MPi-KM variation except for the 5.45x39mm ballistic curve and 800m battlesight pads machined into the top for the rear sight leaf slider. Images are of a 1988 MPi-AKS-74N.
(Image Source: Author)